Step 1 - Create the Ionic Liquid Species
We need to create the cation and anion species for our simulation. Here we’ll just import them from some existing xyz coordinate files that we just happen to have laying around.
1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Cation
First, the 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium cation, which we’ll call “EMIM” for short from here on in:
Species ⇨ Import ⇨ From XYZ…
Choose the
emim.xyzfile.
Rename the species to
EMIM by double-clicking on the tab name
Once you’ve selected the xyz file Dissolve will allow you to perform any last minute edits to the structure should you need to. The principal reason might be to correct the bonding between atoms, which Dissolve automatically calculates when the xyz file is read in.
The structure in the file is fine as-is, so:
Exit the species editor by clicking
Once a species has been created you cannot add or remove atoms or bonds, as these now represent immutable data in your simulation. If you need to change something, you’ll have to create a new species.
The creation of the species is now complete, and should look like this:

The imported EMIM cation structure
For the uninitiated, the EMIM cation is a five-membered imidazole which has been alkylated on both nitrogen atoms (with an ethyl and a methyl group respectively), resulting in a +1 overall charge.
Acetate Anion
Second, the acetate anion, which we’ll refer to as “OAc”.
Species ⇨ Import ⇨ From XYZ…
Choose the
oac.xyzfile.
Again, the structure in the file is fine as-is, so click to accept the structure.
Rename the species to
Acetate by double-clicking on the tab name
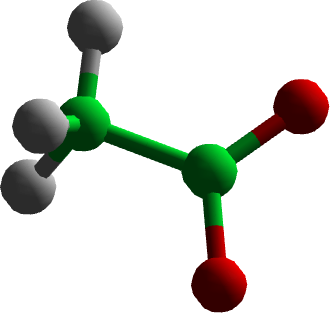
The imported OAc anion structure
And there you have it - acetic acid which has been deprotonated to give us an anion with -1 overall charge to balance out our cation.